Source Definition
The main direction of irradiation is defined be the field, which identifies a frame of reference directed along the beam axis. Thinking of a active scanning device, the accelerator beam is usually deflected with respect to beam axis in order to hit a set of control points in a plane containing the isocentre. At each control point, several parameters are defining the properties of the delivered beam, e.g. the transverse size of the beam, the amount of delivered particles, the energy of the beam, and so on.
In FRED language field and beam are synonyms, and the same is true for pencil beam and beam spot. The pencil beam allows to finely tune all the relevant parameters needed for reproducing a complete irradiation plan (a.k.a. RTPLAN).
The hierarchical structure of fields and pencil beams can be represented in this way
Field_1
├── PB_1
└── PB_2
Field_2
├── PB_1
├── PB_2
└── PB_3
Field_3
└── PB_1
where each field has many pencil beams. A field can be moved around the phantom using the transform: directive. When a field moves, it rigidly brings together all belonging pencil beams. For this reason, the geometrical properties of a pencil beam are defined in the FoR of the referenced field, and not in the Room.
The Quick and dirty setup
Using the default setup (i.e. using Field_0), it is possible to quickly explore the main parameters used to describe a pencil beam (or spot). This approach is recommended for quickly gaining control on how to instruct FRED to deliver particles to a target. In the default setup, Field_0 has a single pencil beam that propagates on-axis, so that actually it is possible to identify the pencil beam with the field itself.
- pbParticle = particleID
type of primary particles delivered by the beam
default = proton
- pbE = (float) [MeV]
pencil beam energy
default = 100 MeV
- pbEu = (float) [MeV/u]
pencil beam energy per atomic mass unit (a.k.a. per nucleon)
- pbPSpread = (float)
fractional momentum spread (FWHM of a gauss distrib)
default = 0
- pbESpread = (float)
fractional energy spread (FWHM of a gauss distrib)
default = 0
- pbXsec = mode
cross-section distribution:
- pbFWHM = (float)
FHWM parameter for cross section distribution (both x and y)
default = 0
- pbFWHMx = (float)
FHWM parameter for cross section distribution (along x)
default = 0
- pbFWHMy = (float)
FHWM parameter for cross section distribution (along y)
default = 0
- pbFWHMa = (float)
rotation angle [deg] of transverse plane for cross section distribution
default = 0
- pbRmin = (float)
particles are generated for r>=pbRmin in the radial direction
default = 0
- pbRmax = (float)
particles are generated for r<=pbRmax in the radial direction
default = inf
The pencil beam
The pencil beam (or spot, beamlet, etc.) describes the properties of a directed source of particles. Each PB is identified by a unique ID and belongs to a given Field.
The position and direction of the PB are given in the FoR of the referenced Field.
The PB parameters can be grouped on the basis of controlled quantity:
A pencil beam definition starts with the pb: directive. Also the multiline syntax pb< .. pb> can be used.
pb: 1 1 ; particle = proton; T = 150; Xsec = gauss; FWHM = 0.5; ...
Some of the parameters are mandatory, which is explicitly marked and the default parameters for the optional are given.
- PBIDpencil beam ID (mandatory)
Number identifying the pencil beam.
- FIDreferenced field ID (mandatory)
Number identifying the referenced field.
Important
Please pay attention to the syntax of pb: directive
pb: PBID FID ; ...The mandatory parameters
PBIDandFIDmust be separated by space, then the list of semicolon-separated optional parameters follows
Particle type and number
- particle = (particle name) [proton]
particle type to be delivered (a.k.a. primary particle). Check the list of available particles using
fred -particles- N = (float) [1]
actual no. of primary particles delivered by the pencil beam (a.k.a. fluence). By default this no. is 1, so that the corresponding dose map is per primary
- nprim = (#) [1e4 = 10000]
no. of Monte Carlo histories to be simulated. This sets the level of statistics used to reproduce the mean dose map of the pencil beam.
Energy and momentum
- T = (float) [100]
(mean) kinetic energy of primary particles [MeV].
- Tu = (float)
(mean) kinetic energy of primary particles per unit mass [MeV/u].
- ESpread = (float) [0]
fractional energy spread (FWHM of a gauss distrib)
- pSpread = (float) [0]
fractional momentum spread (FWHM of a gauss distrib)
Important
Redefinition of some parameters and choice of energy distribution.
New in version 3.59.0
- E | Emean = (float) [100]
(mean) kinetic energy of primary particles [MeV].
- Eu | Eumean = (float)
(mean) kinetic energy of primary particles per unit mass [MeV/u].
- Espread = (float) [0]
fractional energy spread (FWHM of a gauss distrib)
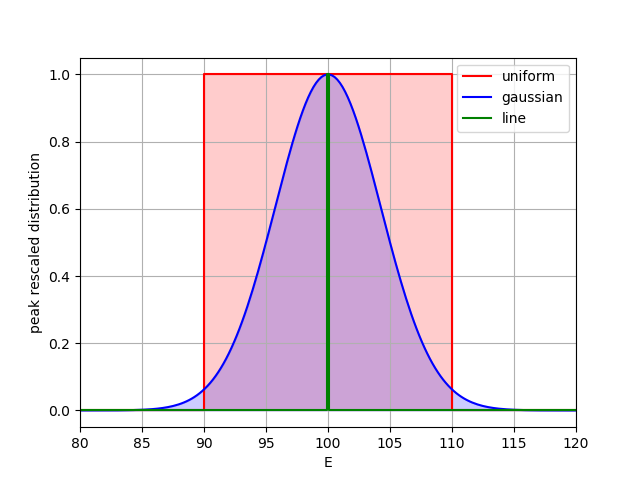
Energy distributions.
Important
- Line source (default)
New in version 3.59.0
- Edistrib = line | monoenergetic | monochromatic
Particle energy is constant (line source).
Note: any other energy distribution with zero width will automatically fall back to the monoenergetic source.
- E | Emean | Eu | Eumean
kinetic energy of primary particles [MeV or MeV/u].
Important
- Gaussian source
New in version 3.59.0
- Edistrib = gauss | gaussian
Particle energy is sampled from a gaussian distribution.
The distribution is defined by its mean value and its width.
The width is defined using the following alternatives: the standard deviation, the FHWM or the fractional spread.
- E | Emean | Eu | Eumean
mean kinetic energy of primary particles [MeV or MeV/u].
- Estdev | Eustdev
standard deviation of gaussian energy distribution [MeV or MeV/u].
- EFWHM | EuFWHM
FWHM of gaussian energy distribution [MeV or MeV/u].
- Espread
fractional energy spread (FWHM of the gaussian distrib)
- Emin | Eumin =0 ; Emax | Eumax = inf
sampling range [MeV or MeV/u].
Portions of a gaussian distribution can be sampled by redefining the default range.
Important
- Uniform source
New in version 3.59.0
- Edistrib = uniform | flat | box | rect
Particle energy is sampled from a uniform distribution.
The distribution range can be defined in two alternative ways, using Emean and EFWHM or specifying the range with Emin and Emax.
- E | Emean | Eu | Eumean
mean kinetic energy of primary particles [MeV or MeV/u].
- EFWHM | EuFWHM
FWHM of energy distribution [MeV or MeV/u].
- Emin | Eumin ; Emax | Eumax
sampling range [MeV or MeV/u].
Position and direction
- P = [0, 0, 0]
Position of the PB with the respect to its field. By default the PB is positioned at field origin.
- v = [0,0,1]
Direction of PB with the respect to its field. By default the PB is directed parallel to the field. This vector is normalized internally to a unit vector.
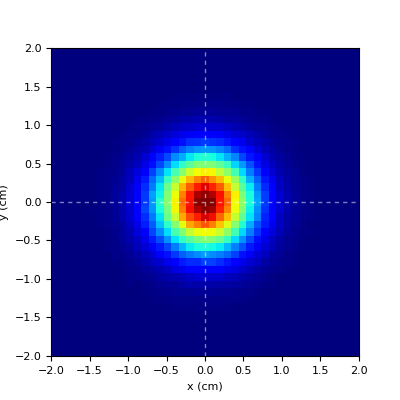
Transverse distribution (a.k.a. cross-section)
- Xsec = (name) [pin]
available options are
- pin|dot
pin-like (FWHM=0)
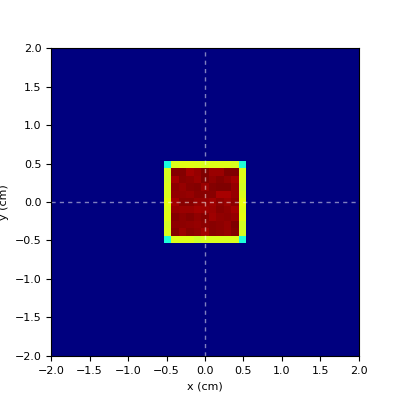
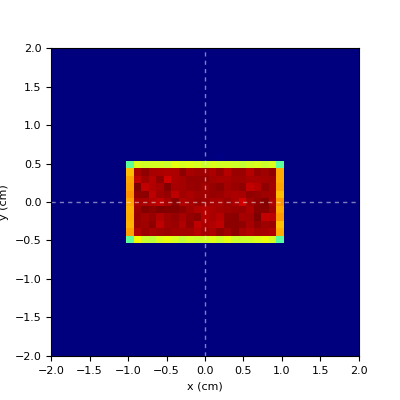
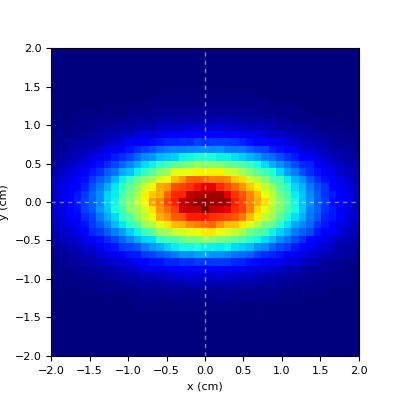
- square|box|rect
uniform square of side = FWHM
rectangular distribution if FWHMx!=FWHMy
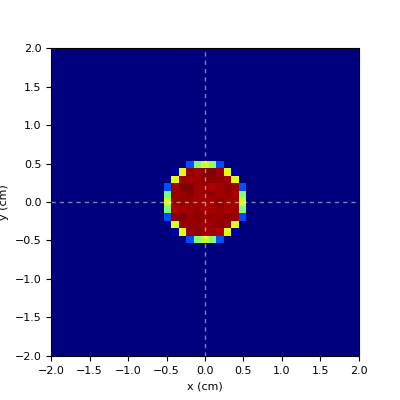
- disc|circle|ellipse
uniform disc with diameter = FWHM
elliptical distribution if FWHMx!=FWHMy
- gauss
gaussian distribution with FHWM = FHWM
bivariate distribution if FWHMx!=FWHMy
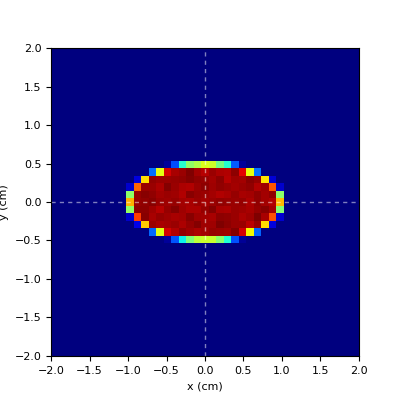
- uparrow
a distribution shaped like an arrow pointing in the up direction. It can be used to check alignment and that the field frame of reference is as expected.
- FWHM = (float) [0]
FHWM parameter for cross section distribution (both x and y)
- FWHMx = (float) [0]
FHWM parameter for cross section distribution (along x)
- FWHMy = (float) [0]
FHWM parameter for cross section distribution (along y)
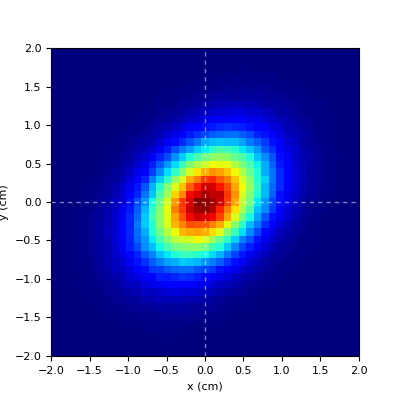
- alpha = (float) [0]
rotation angle [deg] of transverse plane for cross section distribution
- rmin = (float) [0]
particles are generated for r>=rmin in the radial direction
- rmax = (float) [inf]
particles are generated for r<=rmax in the radial direction
Demo of spot cross-section manipulation can be found in this example.
Beam envelope propagation
Three models can be used to describe the evolution of spot size (i.e. its cross-section) along the propagation direction: paraxial, virtual point source and emittance model.
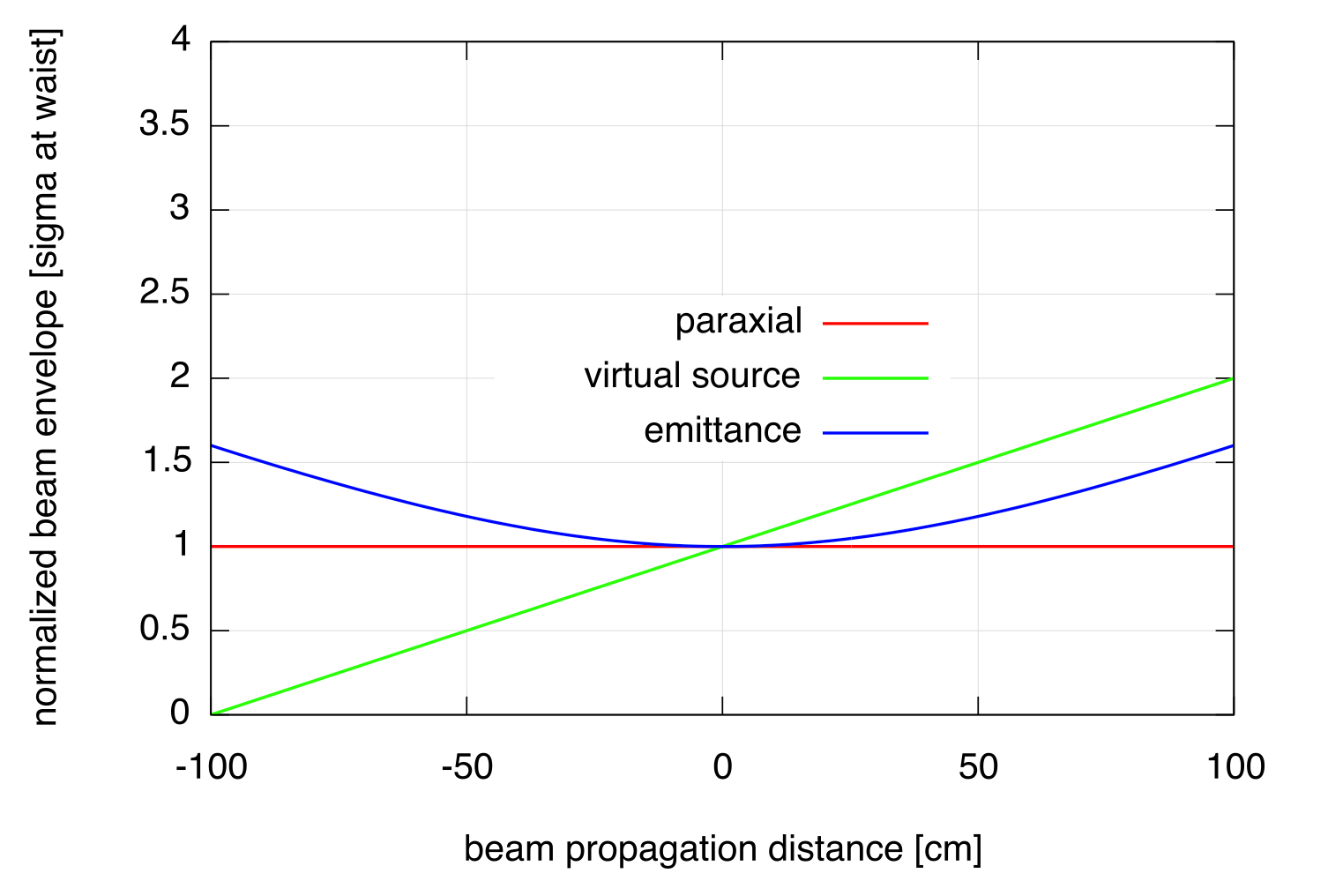
Beam envelope models
By default the propagation is paraxial, namely the particles are propagating along the pencil beam axis. In paraxial mode, the spot size of the beam is constant (see red line in the Figure above).
The Virtual point Source Distribution (VSD) describes a source of particles emitted by a point in space and expanding along the propagation direction with constant divergence (the green line in the Figure corresponds to a virtual source located at x=-100 cm).
The emittance model describes the propagation of a gaussian beam in absence of active elements (deflecting magnets or focussing quadrupoles). It can be used to describe the beam propagation in the last track of an accelerator beamline. In the Figure, the blue line shows a beam focussing and then defocussing, with the minimum spot size at x = 0 cm, also called the beam waist position.
The Sigma Squared is a powerful model that can express all three previous models with a single formalism. The beam envelope can be described with three parameters \(a,b,c\), which are easily obtained from typical spot size measurements taken in a treatment centre as part of the accelerator QA protocol. The parameters can be interpolated from one measured point to another one, as part of a beam model definition.