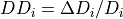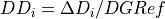Variance Reduction
This module allows to estimate and reduce the statistical error of Monte Carlo (MC) simulations. The strategy applies to the dose map in the phantom.
The MC simulation is split into a series of subsequent iterations, each one tracking a sample of the actual primary particles delivered by the accelerator in the given RTPLAN. By acquiring statistical information after each iteration, the algorithm estimates the mean dose error in the voxel.
Each iteration will produce an estimate 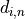 of the dose, where
of the dose, where 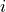 is the voxel index and
is the voxel index and 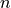 is the iteration index.
is the iteration index.
The mean dose 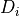 in the ith voxel out of
in the ith voxel out of 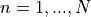 iterations is defined as
iterations is defined as
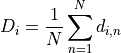
and the standard deviation 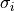 in the ith voxel is
in the ith voxel is
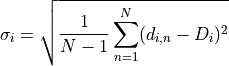
finally the mean dose error in the voxel is given by
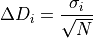
The module computes estimates of the dose mean error for a subset of phantom voxels (see below). By increasing the MC statistics, i.e. the number of traced particles, it is possibile to reduce the statistical MC error below a given threshold.
Using a language borrowed from the gamma-index criterium definition, we define these control parameters
- DCO = dose cut-off (%)
consider only voxels whose dose is larger than DCO percentage of dose global maximum
- DD = dose difference or error (%)
voxels whose dose mean error
is smaller than DD are passing the convergence test
- DDType = GLOBAL/LOCAL
if GLOBAL, the
, if LOCAL the
- DGRef = Dose Global Reference value (Gy)
can be used to prescribe a fixed value for DD evaluation using GLOBAL criterium, i.e.
- maxNumIterations
maximum number of iterations, after which, if convergence has not been reached, the iteration procedure is stopped anyway (default value = see below)
- lStratifiedSampling = (T/F)
use stratification in pencil beam primary sampling, i.e. the number of primary per PB is proportional to the PB fluence (number of primary particles delivered by the accelerator)
- lWriteDoseMeanError = (T/F)
output the map of computed dose mean error in
out/DoseMeanError.mhd- lWriteDoseStdev = (T/F)
output the map of computed dose standard deviation in
out/DoseStdev.mhd
During the iterations, the dose error is reported in the output file, and logged in the out/log/iterations.txt file.
- Three different modes of operations can be used
fixed repeated iterations
recalculation percentage
reduction of dose error until convergence
Fixed repeated iterations
varianceReduction: maxNumIterations=10
In this mode, the simulation is repeated a fixed number of times. By default stratification is off, so the number of primaries per PB is that prescribed by using nprim. If you want to use stratified sampling, you have to require it explicitly
varianceReduction: maxNumIterations=10 ; lStratifiedSampling=t
At the end of iterations, a report on the mean dose error obtained above DCO is given.
Recalculation percentage
varianceReduction: recalculationPrimaryPercentage = 1
The number of simulated primary particles is a given percentage of the total number of primaries delivered by the accelerator in the RTPLAN.
By default the simulation is split in 10 iterations, and stratification is applied.
Dose error reduction
A goal error using DD is specified, and FRED keeps on iterating the simulation until the dose mean error reduces below DD in all the voxel above the DCO.
If convergence is not reached, after a maxNumIterations the iterating procedure is stopped.
varianceReduction<
DD = 1 # 1% dose error
DCO = 50 # consider voxels above the 50% isodose
DDType = G # use the GLOBAL criterium as described see above (default)
maxNumIterations = 100 # default value for this mode
varianceReduction>